Going to digital image space
앞으로 보일 유도들은 pinhole model을 이용하지만, paraxial refraction model에도 적용이 가능하다.
앞서 다뤘듯이, 3D space의 점 $P$는 2D point인 $P^\prime$과 mapping(또는 projected)되었다.
이와 같은 $\mathbb{R}^3\rightarrow\mathbb{R}^2$ mapping을 projective transformation이라고 한다.
하지만, 몇 가지 이유로 image plane으로의 3D points projection은 우리가 실제로 보는 digital image와 direct하게 상응하진 않는다.
- Digital image의 points는 image plane의 points와 다른 reference system에 속한다.
- Digital image는 이산적인 pixel로 이루어져있지만, image plane의 점들은 연속적이다.
- 물리적인 sensor는 distortion과 같은 non-linearity를 유발하기도 한다.
따라서 이와 같은 차이들을 고려하려면, 몇 가지 추가적인 transformation이 필요하다.

The Camera Matrix Model and Homogeneous Coordinates
Introduction to the Camera Matrix Model
Camera matrix model은 어떻게 world point인 $P$ 가 image coordinate인 $P^\prime$에 mapping이 되는지에 대한 몇 가지 중요한 parameter를 포함한다.
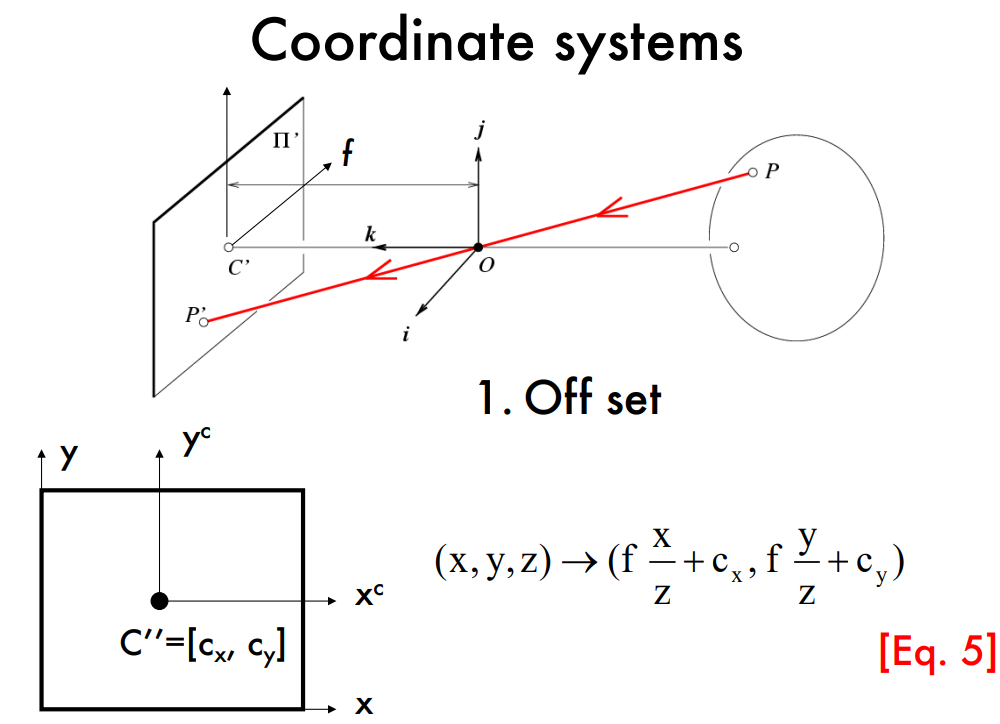
1. $c_x,c_y$
Image plane과 digital image coordinates가 translation에 의해 어떻게 달라지는지를 설명한다.
Image plane coordinates는 중심에 원점 $C^\prime$(k축과 image plane의 교점)이 존재하지만,
digital plane의 원점은 왼쪽밑 끝부분에 있으므로 translation vector $[c_x\,\,\,c_y]^T$ 만큼 떨어져있다.
따라서 아래와 같이 mapping을 정의할 수 있다.
$$ P^\prime=\begin{bmatrix}x^\prime \\ y^\prime\end{bmatrix}=\begin{bmatrix}f\frac{x}{z}+c_x \\ f\frac{y}{z}+c_y\end{bmatrix} $$
2. $k,l$
두 번째 문제점이 digital image의 points는 pixel로 표현된다는 것이었다.
반대로, image plane의 points는 $cm$ 와 같은 물리적 measurement로 표현된다.
따라서 $k, l$ 과 같은 parameter의 경우 $\frac{\text{pixels}}{\text{cm}}$ 과 같은 형태가 된다.
Pixel의 비율이 꼭 같을 거라는 보장이 없으므로 $k$와 $l$은 다를 수도 있다.
만약 $k=l$ 이면 카메라가 square pixel을 가지고 있다고 말한다.
$k,l$ 을 둘 다 고려한 mapping은 다음과 같다.
$$ P^\prime=\begin{bmatrix}x^\prime \\ y^\prime\end{bmatrix}=\begin{bmatrix}fk\frac{x}{z}+c_x \\ fl\frac{y}{z}+c_y\end{bmatrix}=\begin{bmatrix}\alpha\frac{x}{z}+c_x \\ \beta\frac{y}{z}+c_y\end{bmatrix} $$

하지만 아직 $P\rightarrow P^\prime$ projection이 $z$ parameter 때문에 linear 하지 않다.
만약 이 projection이 linear transformation이면 matrix와 input vector간의 product로 표현할 수 있다.
따라서 후에 더 useful한 유도를 위해서는 이 transformation이 linearity를 가지면 더 좋을 것이다.
이를 해결해줄 수 있는 것이 바로 Homogeneous coordinates 이다.

Homogeneous Coordinates
$P^\prime=(x^\prime,y^\prime)$ 이 $(x^\prime,y^\prime, 1)$ 이 되는 새로운 좌표계를 도입한다.
마찬가지로 $P=(x,y,z)$ 는 $(x,y,z,1)$ 이 된다.
이와 같은 augmented space를 homogeneous coordinate system이라고 부른다.
위처럼 Euclidean vector $(v_1,\,...,v_n)$을 homogeneous coordinate인 $(v_1,\,...,v_n, 1)$ 으로 바꾸려면 단순히 새로운 차원에 1을 추가하면 된다.
유의할 점은, 이 vector와 homogeneous coordinates 간의 equality는 마지막 좌표가 1일 때만 성립한다.
따라서 homogeneous coordinate $(v_1,\,...,v_n,w)$ 는 euclidean coordinate으로 $(\frac{v_1}{w},\,...,\frac{v_n}{w})$ 이다.
Homogeneous coordinate를 이용하면, 아래와 같이 표현할 수 있다.
$$ P^\prime_h=\begin{bmatrix}\alpha x+c_xz \\ \beta y+c_yz \\ z\end{bmatrix}= \begin{bmatrix} \alpha & 0 & c_x & 0 \\ 0 & \beta & c_y & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 & 0\end{bmatrix}\begin{bmatrix} x \\ y \\ z \\ 1\end{bmatrix}=\begin{bmatrix} \alpha & 0 & c_x & 0 \\ 0 & \beta & c_y & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 & 0\end{bmatrix}P_h $$
앞으로는, 따로 말하지 않아도 homogeneous coordinate임을 가정하도록 한다.
따라서 이제는 $h$ index를 쓰지 않을 것이고, 없다고 해도 homogeneous coordinates임을 유의하자.
그럼 위의 식을 아래와 같이 표현 가능하다.
$$ P^\prime=\begin{bmatrix} x^\prime \\ y^\prime \\ z\end{bmatrix}= \begin{bmatrix} \alpha & 0 & c_x & 0 \\ 0 & \beta & c_y & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 & 0\end{bmatrix}\begin{bmatrix} x \\ y \\ z \\ 1\end{bmatrix}=\begin{bmatrix} \alpha & 0 & c_x & 0 \\ 0 & \beta & c_y & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 & 0\end{bmatrix}P =MP $$
이 식을 좀 변형해보자.
$$ P^\prime= \begin{bmatrix} \alpha & 0 & c_x \\ 0 & \beta & c_y \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix}\begin{bmatrix}I&0\end{bmatrix}P=K\begin{bmatrix}I&0\end{bmatrix}P $$
이 때, $K$ 를 camera matrix 라고 한다.
The Complete Camera Matrix Model
$c_x,c_y,k,l$ 과 같이 camera의 성질을 나타내는 중요한 parameter들을 위에서 언급했다.
하지만 skewness와 distortion까지 고려해주어야 한다.
1. skewness
Camera의 coordinate system이 skewed 됐을 때(두 축이 90도보다 살짝 더 크거나 작을 때) image가 skewed 됐다고 표현한다.

대부분의 camera는 zero-skew지만 제조과정에서 생긴 불량으로 인해 조금의 skewness가 생길 수도 있다.
skewness를 고려한 camera matrix는 다음과 같다.
$$ K= \begin{bmatrix} \alpha & -\alpha\cot\theta & c_x \\ 0 & \frac{\beta}{\sin\theta} & c_y \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} $$
2. distortion
이 강의에서는 distortion의 효과는 대부분 무시한다.
따라서 camera matrix $K$ 는 5의 자유도를 가진다.
( 2개는 focal length에 의한 $\alpha, \beta$, 2개는 offset 에 의한 $c_x,c_y$, 1개는 skewness에 의한 $\theta$)
위의 parameter들을 intrinsic parameters라고 부르며, 이는 해당 camera에 내재된 unique한 성질이다.
Extrinsic Parameters
실제 3D world가 camera reference system과 같지 않을 수도 있다.
따라서 world reference system을 camera reference system으로 변환하는 transformation이 더 필요하다.

이 transformation은 camera와 무관하므로 extrinsic matrix라고 부르고,
rotation matrix $R$ 과 translation vector $T$ 로 이루어져 있다.

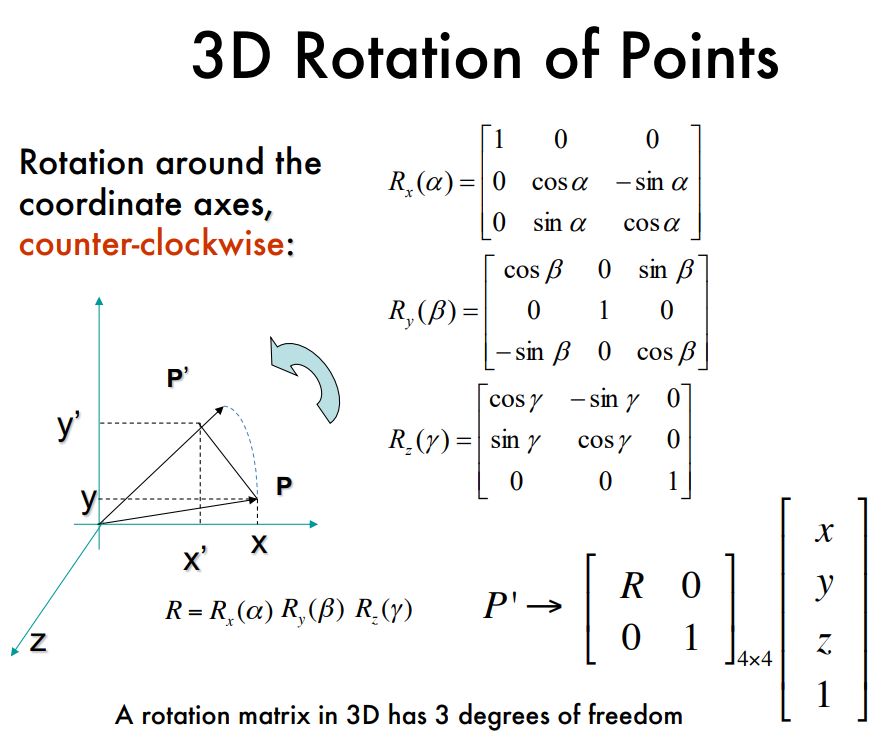

따라서, world reference system에 주어진 점 $P_w$ 로부터 camera coordinate를 계산하면 다음과 같다.
$$ P=\begin{bmatrix}R & T \\ 0 & 1\end{bmatrix}P_w $$
위 식을 이용하면
$$ P^\prime=K\begin{bmatrix}R&T\end{bmatrix}P_w=MP_w $$
와 같이 표현 가능하다.
정리하면, world reference system의 3D point 점 P를 image plane으로 mapping하는 projection matrix M은 2종류의 parameter로 구성되어 있다.
- intrinsic
- extrinsic
이 $3\times4$ 크기의 projection matrix $M$은 11의 자유도를 가진다.
(5개는 intrinsic camera matrix, 3개는 extrinsic rotation, 3개는 extrinsic translation)
'3D\Multiview Geometry > CS231A' 카테고리의 다른 글
| CH02. Single View Metrology (2) (0) | 2023.02.09 |
|---|---|
| CH02. Single View Metrology (1) (0) | 2023.02.08 |
| CH01. Camera Models (4) (0) | 2023.02.06 |
| CH01. Camera Models (3) (0) | 2023.02.06 |
| CH01. Camera Models (1) (0) | 2023.02.05 |
